
Cannabinoids in Cannabis: Here’s What You Need to Know
Cannabinoids in cannabis are not a redundancy. Contrary to what many people think, cannabinoids are not exclusive to cannabis, as we’ll see below.
However, cannabinoids have taken the stage for their role in the hemp industry, most often recognized in the form of THC and CBD. And while many people are comfortable talking about them, the word “cannabinoid” isn’t a part of our everyday vocabulary—but probably should be.
Keep reading to better understand what cannabinoids are, the major cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, and some of their popular uses in today’s world.
What Are Cannabinoids?
As defined by the Alcohol and Drug Foundation, “the word cannabinoid refers to every chemical substance, regardless of structure or origin, that joins the cannabinoid receptors of the body and brain and that have similar effects to those produced by the Cannabis Sativa plant.”
Some of the natural sources of cannabinoids include, but are not limited to:
- Chocolate
- Black pepper
- Rosemary
- Kava
- Broccoli
- Kale
- Cannabis Plant
While cannabinoids can be found in many natural sources, they are often discussed in regard to their role in cannabis products.
Different Types of Cannabinoids Found in Cannabis

So, how many cannabinoids are there in cannabis? There are over 100 cannabinoids (also referred to as compounds) that have been identified. This includes both psychoactive and non-psychoactive cannabinoids with varying benefits.
Major Cannabinoids in Cannabis
A 2012 study identified 4 major compounds found in the cannabis plant:
Delta-9 THC is a major psychoactive compound recognized in cannabis. Delta-9 is the most commonly known form of THC, as it is found more abundantly in the hemp plant, making it cheaper to produce. While a popular cannabinoid, its strong effects can cause negative reactions such as anxiety and brain fog, leading some consumers to prefer Delta-8 as an alternative.
Delta-8 THC is the less potent version of Delta-9, offering consumers a smoother high. Since this cannabinoid is found in smaller traces, it is often extracted from CBD through a process called isomerization.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is another active ingredient that derives from the hemp plant. While it does not have psychoactive properties, it’s recognized for its natural pain-relieving and relaxing effects, making it another popular product on the market.
Cannabinol (CBN) is the less potent version of THC and can produce mild psychoactive effects. CBN is not as commonly discussed, as research on it is more limited than CBD and THC.
List of Additional Cannabinoids
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA)
- Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA)
- Cannabicyclol (CBL)
- Cannabichromenic acid (CBCA)
- Cannabigerovarin (CBGV)
- Cannabivarin (CBV)
- Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA)
Cannabis Cannabinoids Effects
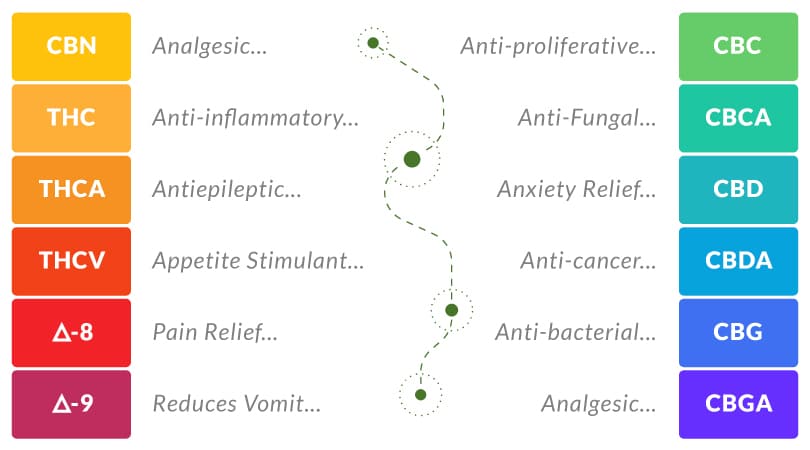
- Delta-9 THC: Highly psychoactive, euphoria, relaxation, pain relief, appetite stimulant, reduces nausea
- Delta-8 THC: Moderately psychoactive, euphoria, relaxation, relieves pain, reduces anxiety, anti-inflammatory
- CBD: Non-psychoactive, improves relaxation, sleep aid, relieves anxiety and pain, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial
- CBN: Mildly psychoactive, sedation, mild relaxation, sleep aid, anti-convulsant
- THCA: Antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory, painkiller
- THCV: Appetite stimulant, antiepileptic
- CBC: Analgesic, antiproliferative
- CBCA: Anti-bacterial, anti-fungi
- CBDA: Anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer
- CBG: Anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory
- CBGA: Analgesic, anti-inflammatory
Recreational, Medicinal & Synthetic Cannabinoids: What’s The Difference?
Recreational
Recreational refers to the use of a product for enjoyment rather than a medical purpose. This may come as no surprise, then, that THC is the most popular recreational cannabinoid due to its psychoactive effects. While it has many benefits of its own, many users seek THC for the “high” that comes with it.
CBD might occasionally be considered recreational by some, even though the legal limit of 0.3% THC is not enough to produce a high. However, many people enjoy the relaxing effects and boost of wellness that it contributes to their routine.
Medical Use of Cannabinoids
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health claims that drugs containing cannabinoids may be helpful in treating certain rare forms of epilepsy, nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy, and loss of appetite and weight loss associated with HIV/AIDS, as well as chronic pain and multiple sclerosis symptoms.
While there are many cannabinoids that can contribute to the world of medicine, the most notable are CBD and THC. In our blog, we explore a range of topics that are related to the benefits of consuming full-spectrum CBD and Delta-8 THC, including their role in nausea, migraines, pain, getting a better night’s sleep, muscle spasms, and more.
Synthetic Cannabinoids
Synthetic cannabinoids are laboratory-made substances. These substances typically have a bad reputation, as they undergo chemical processes that can expose consumers to toxic substances.
However, the word “synthetic” can also be used to refer to products that are made from other naturally occurring cannabinoids. Let us explain.
Remember when we said that Delta-8 was extracted from CBD because it is found in smaller quantities? Well, there’s much debate over whether Delta-8 is synthetic. While it’s a naturally occurring cannabinoid, it undergoes a process to turn CBD into Delta-8.
This allows more consumers to enjoy the benefits of Delta-8 THC, but the process must be done carefully to guarantee quality.
The Entourage Effect
A 2020 study defines the entourage effect as “the suggested positive contribution derived from the addition of terpenes to the effect of cannabinoids. This means that the entirety of the effect is greater than the sum effects of its contributing parts.”
This isn’t to say that the isolated compounds don’t have their own benefits, but rather that the effects are maximized when all of the compounds in the plant work together.
The three players at hand are cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids.
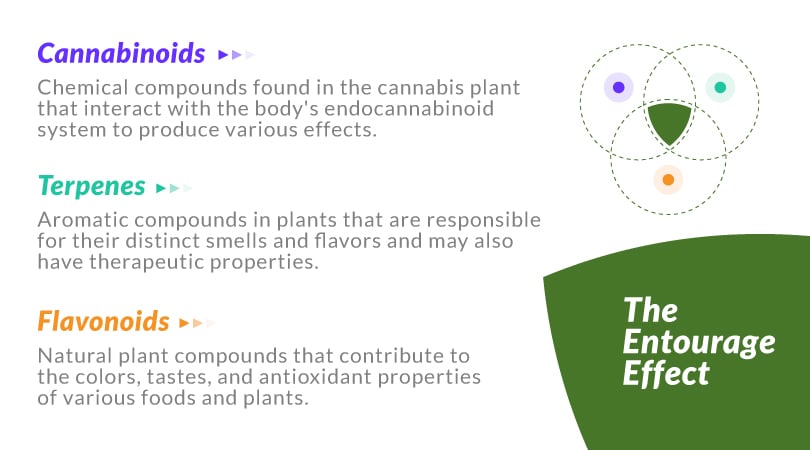
Cannabinoids: Chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce various effects.
Terpenes: Aromatic compounds in plants that are responsible for their distinct smells and flavors and may also have therapeutic properties.
Flavonoids: Natural plant compounds that contribute to the colors, tastes, and antioxidant properties of various foods and plants.
A 2011 review of studies found that taking terpenes and phytocannabinoids together may be beneficial for pain, anxiety, inflammation, epilepsy, cancer, and fungal infections.
To achieve the entourage effect, individuals must seek out products that contain all of the compounds of the cannabis plant, which are referred to as full-spectrum products. While looking for products, the box should clearly state what type of product it is; check out the image below to get an idea of what you should look for.

Vitality’s full-spectrum CBD oil gives consumers the opportunity to maximize the benefits of cannabinoids by combining CBD, THC, and other important compounds that are naturally found in the cannabis plant.
The Future of Cannabinoids in Cannabis
While cannabis has been used for thousands of years, more research is required to understand how cannabinoids can be used for maximum benefits.
In the past two decades, researchers have taken steps to figure out how cannabinoids affect our bodies. As explained above, cannabinoids are already being used in the medical world, but it’s expected that more studies will be performed to understand how they can be incorporated into our health and wellness routines.
Final Thoughts
Cannabinoids are naturally found in many plants but have recently earned a spotlight for their role in the cannabis plant. With over 100 cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, the most famous are THC and CBD, though every cannabinoid is important in creating the entourage effect.
As more research is performed, it’s believed that cannabinoids can be incorporated even more into the medical world, offering benefits to many patients. As more information is released, we’ll continue to update our blog with relevant information.
References
Atakan, Z. (2012a). Cannabis, a complex plant: different compounds and different effects on individuals. Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology, 2(6), 241–254. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045125312457586
Cannabinoids – Alcohol and Drug foundation. (n.d.-a). https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/cannabinoids/#:~:text=What%20are%20cannabinoids%3F,by%20the%20Cannabis%20Sativa%20plant.
Cannabis (Marijuana) and Cannabinoids: What You Need To Know. (n.d.-a). NCCIH. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cannabis-marijuana-and-cannabinoids-what-you-need-to-know#:~:text=Are%20cannabis%20or%20cannabinoids%20helpful,loss%20associated%20with%20HIV%2FAIDS.
Ferber, S. G., Namdar, D., Hen-Shoval, D., Eger, G., Koltai, H., Shoval, G., Shbiro, L., & Weller, A. (2020a). The “Entourage Effect”: Terpenes Coupled with Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Mood Disorders and Anxiety Disorders. Current Neuropharmacology, 18(2), 87–96. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159×17666190903103923
Russo, E. B. (2011a). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology, 163(7), 1344–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01238.x
